Risk management: There is no need to fear PEST
Hello. This is Irino, a strategy consultant.
I will summarize the points to keep in mind regarding risk management in relation to business planning and provide you a powerpoint sample for downloading.
The positioning of Risk management
- Executive summary
- Background
- Management team
- Company overview
- Management and business principles
- Product/service overview
- How your profits are made
- Analysis of the market and the competitors
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Operation plans
- Personnel strategies
- Start-up strategies
- Growth strategies
- Exit strategies
- Financial plans :
– Sales forecast
– Cost plans
– Financing forecast
– Capital policies - Risk management
- Project management
PEST is a framework that is often used to analyse external environment.
| Politics: | Change of administration, law, regulations, permission and authorization. |
| Economics: | Economic trend, interest-rate trend, currency exchange rates, employment trend. |
| Society: | Culture, demographics, boom, consensus. |
| Technology: | New technologies, invention, infrastructure. |
I often come across business plan documents that use the PEST framework to write a risk management section. However, it has some problems.
- There external environmental factors are too “macro” for venture and smaller companies, so even if risks are recognized, you wouldn’t be able to come up with concrete measures to tackle them.
- Managers seem to say that the reason their business is likely to fail is due to external factors.
It is OK to write PEST in order to provide an outline of the industry to investors or give a big picture of the business as a manager. However, if you want to manage risks, then PEST alone is absolutely insufficient. People will easily tell that you don’t think well of the risk management. It’s important to look at risks not only from macro perspective, but micro perspective as well. You also want to make sure that internal environmental risks which venture companies can take measures to are also included and considered.
- Risk concerning fund management
- Risk of client companies going bankrupt
- Risk of starting members/staffs breaking away
- Risk of major corporations getting in the same business
- Risk of not receiving enough financing and investment
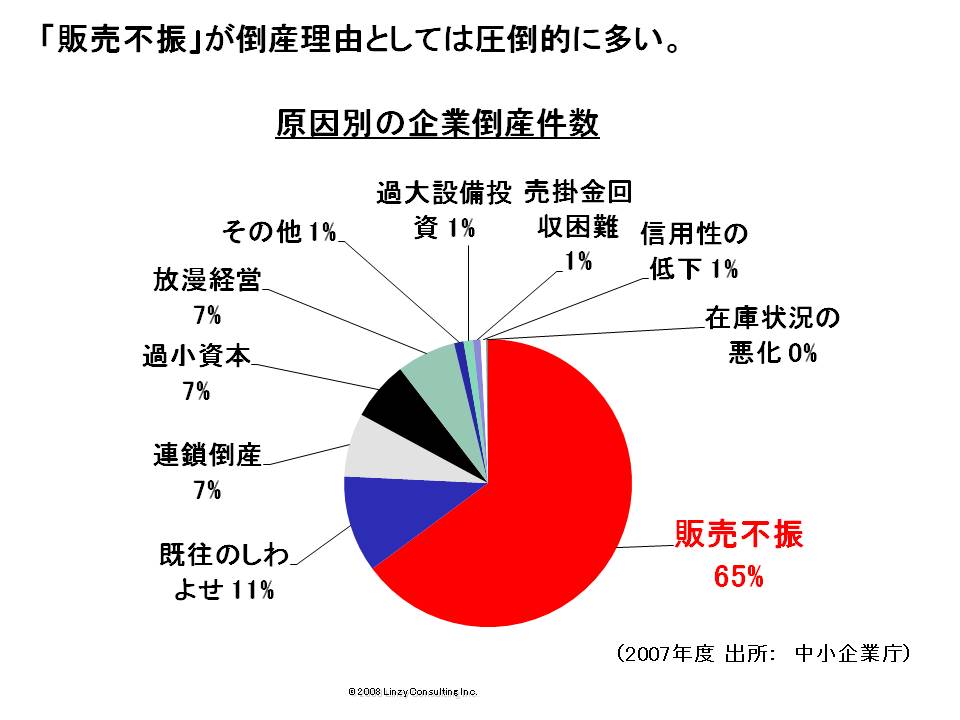
There risks are often mentioned. However, risk of bad sales performances are not included in business plan documents often. According to the statistics given by small and medium enterprise agency, the reasons why Japanese companies go bankrupt are as follows.
You need to pay a close attention to bad sales performances. It’s 65% and by far the most common cause of bankruptcy. From my experience, the ones that are guessed wrongly frequently are sales prediction.
Therefore, you should include bad sales performance in the risk management section. Experienced investors most probably would think that you don’t have much experience as a manager and not know the reality, so you want to watch out.
There is no need to include things that you “normally would do to promote sales or to reduce quality related risks” in your risk management section. They should be written in your “marketing and sales strategy policies” or “operational planning (quality management plans)” section. The information which needs to be included is:
- Measures that would go wasted if no risks ever take place.
- Measures that require costs, man-hours, and are time-consuming.
For example,
- Make sure to get involved with a part time project to get daily earnings besides what you really want to do.
- Even if you are getting sufficient income from company A, to prepare yourself against their poor business performance, develop a business relation with company B as a backup.
- Collecting accounts receivable will be costly, so use electric withdrawal.
I know some venture companies overly avoid risks and miss out on opportunities. Risks tend to be avoided or cut down, but also they can be accepted. For example, a lot of major corporations avoid risks from law and regulations by reason of their uncertainty. However, they are obviously great and right business opportunities for venture companies. The point is:
- Don’t cause people some trouble or exploit them in order to gain profits.
Such business will not be profitable in the long run. - Don’t neglect the task of checking with government offices.
People often consult with lawyers first. Lawyers can give you legal points to keep in mind, but they can’t make the final decision for you. It’s quicker if you just called regulatory authorities.
Various people will approach venture companies that are starting to succeed. If you have business relations or capital ties with dubious people, it could be a knock out factor when you take your company public. Experienced managers
- have enough life experience to see through people.
- have a wide human network to check the careers of dubious people.
I want you to look at the demographic chart of why Japanese companies go bankrupt once again.
I would like you to pay attention to “strains caused previously”. It is 11% and the second most common reason of bankruptcy. It’s a case in which companies go bankrupt because they don’t understand the meaning of concrete numbers which are brought about by crisis level bad performances. Experienced managers
- know concrete managerial indexes.
- define risk triggers.
- take practical measures as soon as possible.
“When is your business likely to fail?”
I know it’s rude to ask such a question to CEO of companies when they are putting all they’ve got into their businesses, but I sometimes dare to ask it anyway. Experienced managers will answer as follows.
“When the unit price of product A decreases by 500 yen and if our monthly sales gets below 20,000 units, then we’re in a bad condition. In this scenario, we will have to work hard on our service B as a part time job to get through.”
Good managers strongly have managerial indexes, a sense of danger and determination to recover the situation no matter what.
That’s it for today.
- A celebrity entrepreneur
- A managing director in a listed company
- A professor
- A rocket scientist
Looking forward to working with excellent leaders.
Please contact:
iphone: 090-6497-4240
irino@linzylinzy.com (Irino)
- One-two finish in the largest business plan contest in Japan
- One-two finish in Asian Entrepreneurship Award
- No.1 in google "business plan"
- Judge in the Cloud-Computing Awards
- Write/Review +100 business plans a year
- Meet +300 entrepreneurs a year
- Large-scale project management
e.g. +15,000 man-months post merger integration - Expertise: business planning, financing, IT, project management
- Fortune Global 500 companies:
bank, brokerage, card, SIer, etc - Startups:
IT, cloud, bio, cosmetics, minor metals, aerospace, etc - Tokyo University -> University of British Columbia -> Oracle -> Headstrong -> Independent
Download a powerpoint of risk management.

Aspects of risk management have been integrated into the financial planning section. I have assumed three scenarios: optimism, pessimism and the middle way and explained the pessimistic scenario in detail.