Growth strategy: Believe other people can do better
Hello. This is Irino, a strategy consultant.
I am going to explain how to write about growth strategy in your business plan documents. This section is about business expansion phase (2~3 years after foundation).
The positioning of growth strategy in your business plan document.
- Executive summary
- Background
- Management team
- Company overview
- Management and business principles
- Product/service overview
- How your profits are made
- Analysis of the market and the competitors
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Operation plans
- Personnel strategies
- Start-up strategies
- Growth strategies
- Exit strategies
- Financial plans :
– Sales forecast
– Cost plans
– Financing forecast
– Capital policies - Risk management
- Project management
Growth actually can be categorized into the following performance goals.
・ Sales volume
・ Pretax profit
・ Current term profit
・ The number of employees
・ The number of shops
・ Monthly surplus
・ Paying off accumulated debts
・ Recognizability
・ Reputation in the industry
And so on.
However, you want to remember that it is impossible to achieve all performance goals at the same time no matter how excellent your venture company is.
Let’s take “Sales volume” vs “Monthly surplus”. Even Amazon, the venture company hero, had to deal with chronic deficit balancethough their sales volume was increasing. They were severely criticized by investors and analysts.
How about “The number of shops” vs “Paying off accumulated debts”? Restaurants often fundraise and open many outlets before they finish paying their accumulated debts for their first stores if they are doing well business wise.
The important thing in this section is to define which performance goals to aim for and which ones to do away with.
There are many business managers who seek new business chances on top of their already successful businesses. Their venture spirits are great. However, it becomes problematic when they try to start businesses which is new and unfamiliar (with their network, technology, know-how, customer list). This is not recommendable because unfamiliar businesses have very low success probability.
Let’s use a yearly deal flow of a big venture capital company as a reference to see the success probability of a new business.
1. Interest investors enough to hear about them: 12,000 companies
2. The level in which companies make it to due diligence stage: 400 companies ≒ 3%
3. The level in which companies actually do receive investments: 90 companies ≒ 0.7%
4. IPO or happy Buyout is less than one second of level 3 ≒ 0.3%
As you can see, success probability of new businesses is three in a thousand. It is not desirable to allow these three successful companies to have fatal risks again. So, here is a diagram that explains what to do.
↓
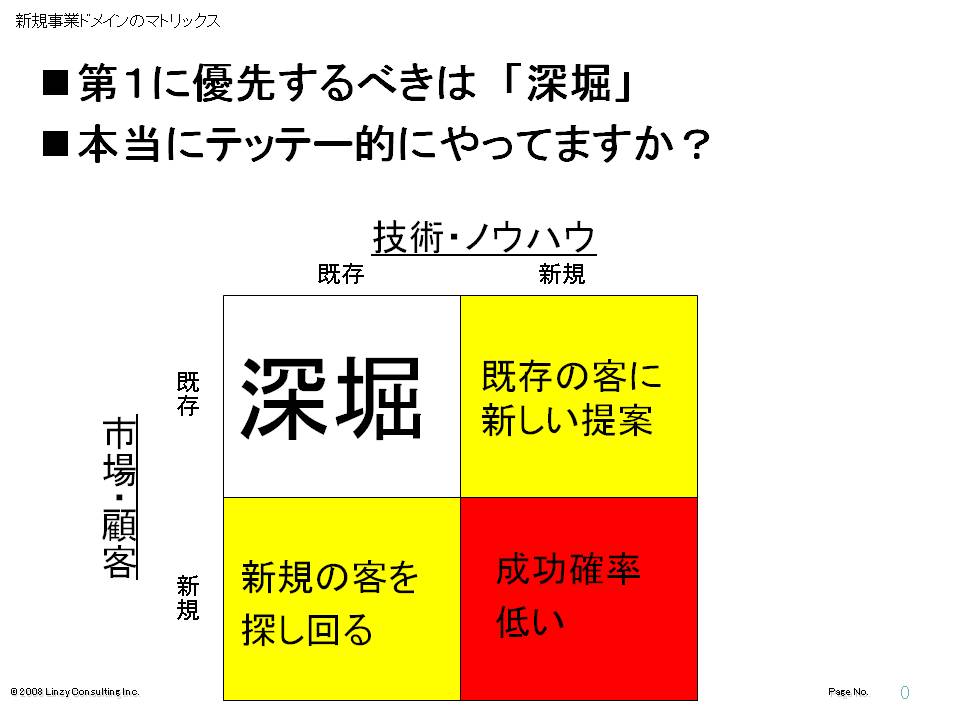
The first thing is to do thoroughly everything you can do. You should think about how to keep providing existing products and technological know-how to existing customers. I have come to learn that many business managers claim that they have worked enough on existing businesses and customers and it is time to challenge a new business in order to grow. However, there are no business domains in this world that small venture companies only 2 or 3 years after launch can do everything for them. Maybe in reality, they are not doing things thoroughly enough. Also, starting a completely new and unfamiliar business from scratch may seem like a positive thing to do, but it is just an all-too-easy evasion.
There are two types of business managers. Those who are good at building from 0 to 1 and those who are good at building from 1 to 100. Those who are good at building from 0 to 1 usually have strong personalities as founders and they have well-developed sales skills and so on. Those who are good at building from 1 to 100 usually have worked for administrative departments of big companies and know how to manage very well.
Advanced people know which type they belong to and certainly their limits as well. Some even cede their presidential positions because they believe other people can do better than themselves. A good example is Google’s founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin. They welcomed Eric Schmidt as their CEO because he had a lot experiences. Google entered its growth phase and the founders just realized that they had neither the skills nor experiences to run a big company organization. So, they resigned their presidential positions and passed the torch to a business manager who was good at building from 1 to 100. Well, Google’s growth is far beyond 100 as you know.

Just the other day, 2 business plans that I was helping with got investments from Angel. I am convinced what is important is not just your business plan’s economic rationality, but extra elements like your passion or being blessed with meeting the right people.
That’s it for today.
Irino
- A celebrity entrepreneur
- A managing director in a listed company
- A professor
- A rocket scientist
Looking forward to working with excellent leaders.
Please contact:
iphone: 090-6497-4240
irino@linzylinzy.com (Irino)
- One-two finish in the largest business plan contest in Japan
- One-two finish in Asian Entrepreneurship Award
- No.1 in google "business plan"
- Judge in the Cloud-Computing Awards
- Write/Review +100 business plans a year
- Meet +300 entrepreneurs a year
- Large-scale project management
e.g. +15,000 man-months post merger integration - Expertise: business planning, financing, IT, project management
- Fortune Global 500 companies:
bank, brokerage, card, SIer, etc - Startups:
IT, cloud, bio, cosmetics, minor metals, aerospace, etc - Tokyo University -> University of British Columbia -> Oracle -> Headstrong -> Independent



